Panorex
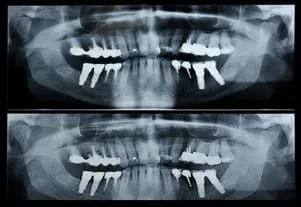
1. Fractures of the teeth and/or jaws can be seen when it is difficult to open the mouth.
2. Viewing development, position, and eruption of primary teeth so we can see all of a child’s baby teeth and permanent teeth at one time
3. For individuals who have difficulty holding x-ray films in their mouth
4. Diagnosing temporomandibular joint (jaw hinge) dysfunction
5. Viewing impacted wisdom teeth
6. Detecting presence of bone or gum diseases
7. Diagnosing early signs of oral cancer
8. Discovering nonmalignant tumors
9. Surveying the sinus region
10. Discovering stones in the salivary glands
11. Examining trauma patients
12. Screening for stroke, osteitis deformans, hyperparathyroidism and other systemic diseases
13. Obtaining baseline data for long term dental health
14. Diagnostic data for a referring dentist to use
15. Critical for setting broken facial bones
16. Identification in case of an accident
17. Provide signs of carotid calcification. Alveolar bone loss is sometimes associated with cardiovascular diseases.
18. Evaluation for full or partial removable dentures, dental implants, or braces.
19. New patients to help screen for diseases beyond just the teeth.
20. Screening for osteoporosis
21. Metastases. Carcinomas of the breast, lung, prostate, thyroid gland, kidney, and colon may produce cyst-like growth in the jaw.
22. Genetic abnormalities
23. Developmental abnormalities like cleft palate
24. Asymmetry of the oral and maxillofacial area which could be caused by swelling on one side of the face as seen in eating disorders.
25. Altered nerve sensation-paresthesia in lip, or hypersensitivity which could be caused by infectious osteomyelitis or a malignancy compressing a nerve
26. Finding the cause and location of pain
27. Ill-fitting dentures due to alveolar bone loss
